General informations
Jelix is a framework for PHP5, whose objective is to ease the development of applications or Web sites of any kind.
Here is what is proposed to developers:
- API dealing with numbers of technical aspects: data access, MVC model, templates, output format generators (HTML, XUL,…), Web services (xml-RPC, json-RPC), forms generator, CRUD, authentication, rights management, localization, etc…
- a modular structure and an organization of the files of the project, imposing a framework and some developing standards.
- a “layer” organization of the project: presentation, coordination, service, business, persistence.
These characteristics allow a better re-use of the code, a capitalization of know-how, a better organization in the development, leading to a better productivity.
Jelix uses to the maximum of specificities of PHP5, in order to be the lightest and most powerful possible. This is why a project based on Jelix is 100% object oriented.
Features
Original functions and characteristics
- Modular architecture : an application can be cut out in several reusable modules.
- Minimal guarantee on the data exchange : Jelix controls the generation of output formats according to the type of request. For example, if we have a request for a XML-RPC web service, we cannot generate HTML, the answer will be obligatorily in XML-RPC. Si it offers a certain robustness of the application in client/server communication. (Unless the developer does not use objects from Jelix, because indeed nothing prevents from making an echo of anything anywhere).
- Generation of technical errors in specified format : thanks to the Jelix system described before, all the technical errors are returned in the format awaited by the client. For example: no HTML formatted error when client is awaiting XML-RPC or RDF response.
- Light and evolutionary template engine (jTpl), with a syntax halfway between Smarty and PHP. A plugin system like in Smarty is also available.
- jDao, object-relational mapping, based on the DAO design pattern (Data Access Object). Declared in XML files, automatic generation of its SQL requests , handling of security problems (SQL injection etc…).
- Designation of files and resources by selectors, and not by physical ways, then bringing a certain independence to a module towards the installation.
- Event system allowing module-to-module communication.
- Overload file : it is possible to redefine some files of a module without changing the originals (DAO, templates, properties). Useful when a module is used by several applications at the same time, or to facilitate the update of a third module.
Modern functions and characteristics
Functions that we don’t find so often in frameworks:
- Web Services : Jelix deals with analysis of the content of requests, and the generation of the response. XML-RPC and JSON-RPC are handled. Other types of services Web are completely possible (SOAP,…).
- Handling of RESTfull : by simple implementation of an interface: one can easily define what is done after HTTP GET/POST/PUT/DELETE requests.
- Themes system: it is possible to define several templates, each one redefining the template of modules.
- Automatic system for URL generation and mapping : no complete URL in Jelix. The framework has the responsibility to generate urls in the templates or elsewhere, according to the configuration of URL mapping defined on actions (mod_rewrite & co).
- PHP scripts for code generation to execute in command liner, allowing fast creation of various files of a project (module, DAO, template, controller, etc)
- Technical cache system : almost all non PHP files of a Jelix project “are compiled” in PHP in order to improve the performances (templates, DAO, events etc.).
- UTF-8 compliant: it's the default encoding of the framework
- Module dedicated to unit tests: unit tests are essentials to create a reliable application. So Jelix provide a module which has an interface to launch unit tests and a simple way to create unit tests (using simpleTest)
Traditional functions and characteristics
Functions which one finds in many frameworks:
- The architecture of the core is MVC type (Model-View-Controller). A coordinator handles the execution of an action according to the parameters in the URL. The possible actions are implemented in classes of jController type (controllers).
- Jelix provide several output generators (jResponse objects): XHTML, CSS, ATOM, RSS, XML, RDF, XUL, XUL overlay, ZIP, PDF (from Latex source files or with TCPDF). Others formats are also possible.
- Database access abstraction layer: jDb relies on PDO or its own classes (when PDO is not available) to access to the databases.
- Localization: you can have your application translated in several languages. Storage of localized string is done in properties files.
- System of authentication and rights management.
- Use of XML: declaration of the events, DAOs etc, … That makes it possible to facilitate writing, generation and modifying these parts of a project by third-party tools (for example with JelixEclipse, an eclipse plugin), and thus to increase productivity.
How does Jelix work
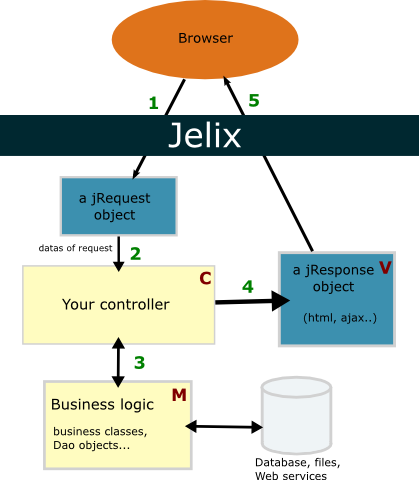
- an HTTP request calls Jelix. Jelix creates an instance of a jRequest object which contains datas of the request. It then create an instance of your controller which corresponds to the asked action.
- A method in the controller is executed. It retrieves request parameters in order to know which process to run.
- Then the method execute business processes and retrieves eventually some results which will be used for the response
- The method of the controller create an instance of a jResponse object which is setup with datas or else (initialization of templates etc..).
- Jelix gets this jResponse object, launch the generation of the final document (html page, pdf..) and then sends it to the browser.
No comments:
Post a Comment